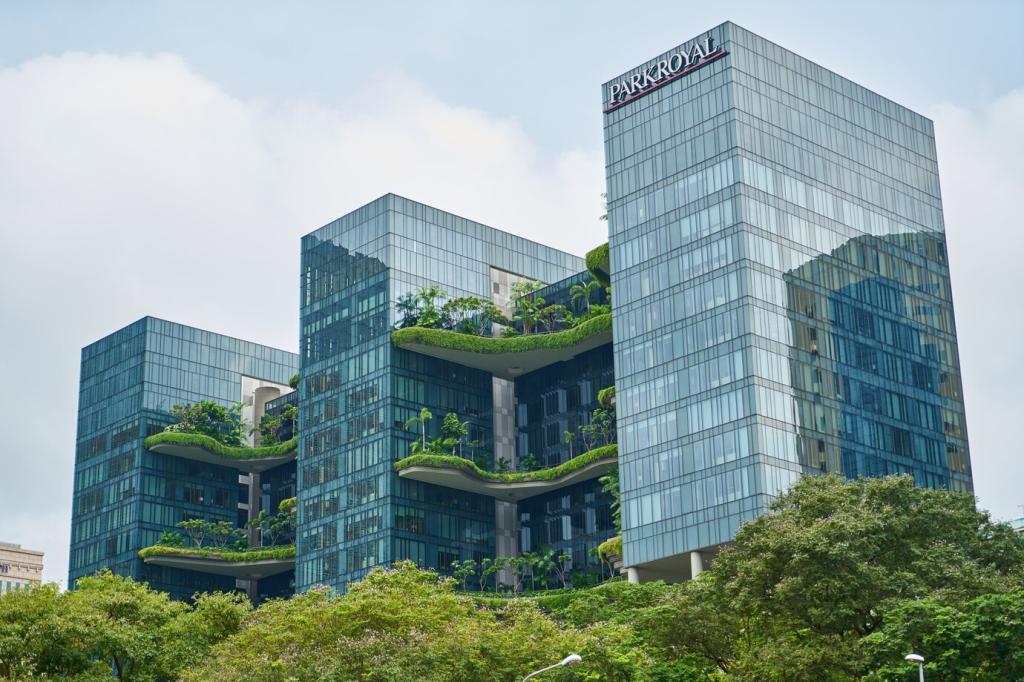
Explore the world of energy-efficient home designs, where sustainability meets modern comfort. Energy-efficient homes are crafted to minimize energy use, reduce environmental impact, and cut utility costs, all while ensuring a comfortable, stylish lifestyle. From smart architectural concepts to the latest in eco-friendly materials and systems, discover how these innovative design solutions are helping homeowners build a greener future.
Optimizing Home Orientation and Layout
When designing an energy-efficient home, where and how your home sits on the property matters tremendously. Strategic placement means orienting the main living spaces so they receive the most natural light throughout the day, particularly in colder climates where sunlight can contribute to home heating. By analyzing the sun’s path, homeowners and designers can reduce the need for artificial lighting and heating, resulting in lower energy bills all year long. This approach not only benefits energy performance but also creates brighter, more inviting interiors. Professionals often recommend placing large windows on the south-facing side and considering minimal windows on the north to retain heat and take full advantage of passive solar gain.
A crucial element of home comfort is indoor air quality, and energy-efficient designs harness architectural features to promote natural ventilation. Well-placed windows, vents, and open-plan layouts enable breezes to flow through living spaces and eliminate stagnant air. By channeling prevailing winds through the home, temperature extremes are moderated without relying heavily on mechanical cooling or heating. Not only does this contribute to energy conservation, but it also creates a continually fresh and comfortable atmosphere. Cross-ventilation, when implemented successfully, can stave off the need for air conditioning during the milder months, contributing to long-term sustainability.
An intelligent floor plan goes far beyond aesthetics; it can greatly impact your home’s energy profile. Zoning refers to grouping rooms and areas with similar temperature and lighting needs together. For instance, putting bedrooms away from the sunniest part of the house keeps them cooler for sleeping, while living rooms can be situated where they’ll benefit from warmth and sunlight. Separating spaces with doors or insulated walls also allows for precise control over heating and cooling, so energy isn’t wasted on empty or infrequently used rooms. Such thoughtful spatial planning not only increases comfort but also adds to year-round savings.
Advanced Building Materials and Insulation
One of the most impactful ways to conserve energy in a home is through superior insulation. High-performance insulation materials—such as spray foam, rigid foam boards, and advanced fiberglass—form a protective barrier that slows the transfer of heat between the inside and outside. By maintaining a steady interior temperature, these insulation systems drastically reduce the load on heating and cooling equipment, resulting in both cost savings and a smaller carbon footprint. Insulation is especially vital in attics, walls, and basements, where the most heat loss or gain typically occurs. The latest options offer improved resistance to moisture and pests, ensuring durability and preserving performance over time.
Integrating Renewable Energy Systems
Solar panels are among the most recognized and accessible renewable energy resources for homes today. Modern photovoltaic systems can be installed on rooftops or as ground arrays, converting sunlight into clean electricity. When tailored to a home’s energy demands and local climate, solar systems can supply a significant portion—or even the entirety—of household electricity needs. With the integration of batteries for energy storage, homeowners can utilize solar power even when the sun isn’t shining. Solar water heaters and passive solar designs further extend the benefits, reducing both power consumption and monthly expenses.